Indian lunar spacecraft records impact of solar flares on moon for first time
Source: Dailynewsegypt | Original Published At: 2025-10-23 10:38:59 UTC
Key Points
- India’s Chandrayaan-2 orbiter recorded the first real-time impact of a solar coronal mass ejection on the moon’s surface.
- The lunar exosphere's pressure and density increased over tenfold during the event, as observed by a special instrument.
- The study confirms the theoretical impact of solar flares on the lunar atmosphere, enhancing understanding of space weather effects.
- Findings are critical for future lunar missions and establishing scientific bases, requiring consideration of solar phenomena in facility design.
- Chandrayaan-2, launched in 2019 by ISRO, is India’s second lunar exploration mission.
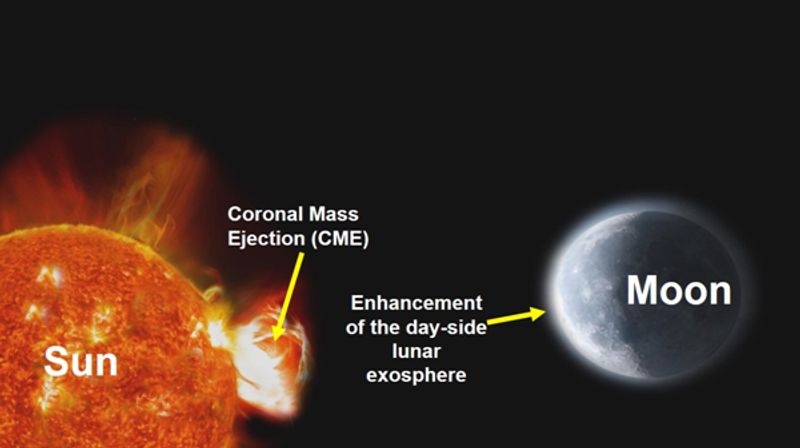
India’s Chandrayaan-2 orbiter has, for the first time, recorded in real time the impact of a solar coronal mass ejection on the moon’s surface, a finding that could be crucial for future astronaut missions, Asian News International, a partner of the TV BRICS network reported.
The observation, conducted using a special instrument, showed that the pressure and density of the lunar exosphere increased more than tenfold during the event, according to Asian News International (ANI).
The lunar exosphere is an extremely rarefied atmosphere where atoms and molecules hardly interact. It is formed by solar radiation, solar wind, and meteorite impacts on the surface. During coronal mass ejections, significant volumes of helium and hydrogen ions are directed towards the moon, affecting the release of particles from its surface and increasing the exosphere’s pressure.
The observation by Indian scientists has confirmed the theory of solar flare impact on the lunar atmosphere. Researchers believe the data will help improve the understanding of the exosphere and the effects of space weather on the moon.
The results are also of practical importance for building scientific bases on the moon, as such extreme solar phenomena can temporarily alter the lunar environment, a factor that must be considered when designing facilities and planning research activities.
Chandrayaan-2 is the second automatic interplanetary station launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to study the moon. It was launched in 2019.